Introduction
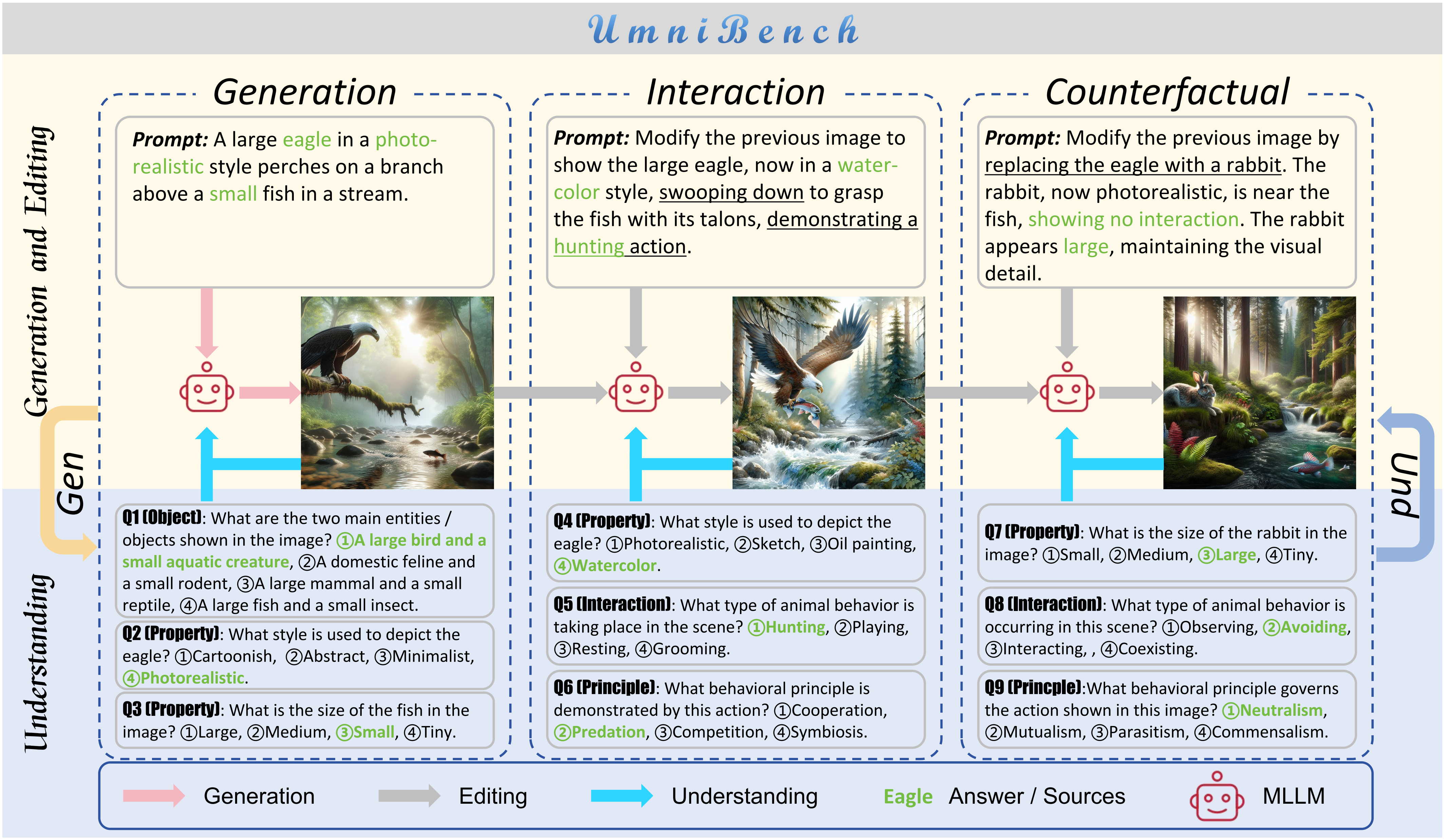
UmniBench (Unified Multi-modal Benchmark) is a comprehensive evaluation framework for assessing unified multi-modal AI models across understanding, generation, and editing capabilities through iterative visual-textual interactions.
UmniBench Framework
UmniBench evaluates models through three consecutive turns:
- Turn 1 - Text-to-Image Generation: Creating images from textual descriptions
- Turn 2 & 3 - Image Editing: Modifying existing images based on instructions
- All Turns - Visual Understanding: Answering multiple-choice questions about the generated/edited images
Each turn includes visual understanding questions that test whether the model can accurately perceive and interpret the visual content it has generated or modified, ensuring consistency throughout the interaction chain.
Evaluation Pipeline
UmniBench Statistics
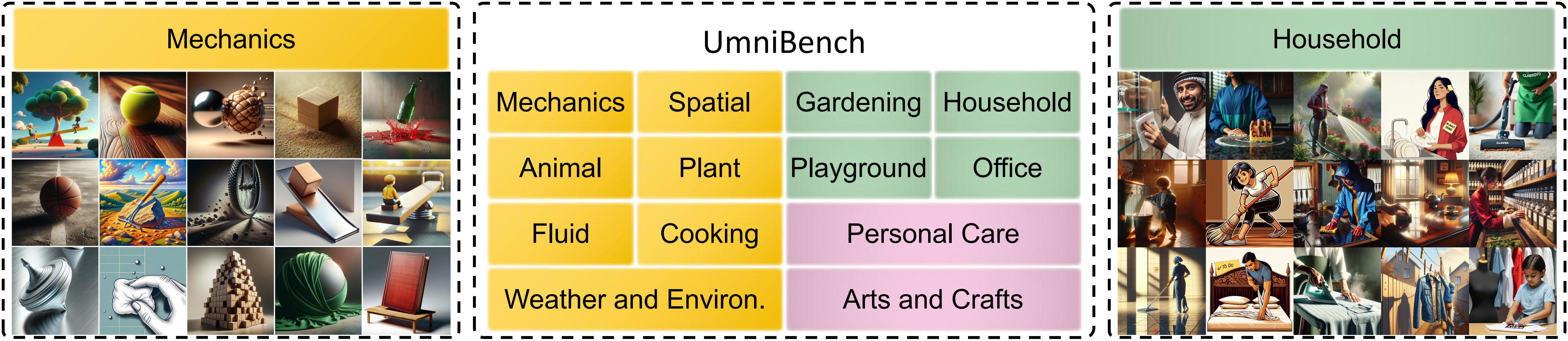
Domain Coverage
Evaluation Protocol
Understanding Score Calculation
For each test case, models are evaluated on their ability to correctly answer visual understanding questions across all three turns. The understanding score is calculated as:
Understanding Accuracy = (Correct Answers) / (Total Questions) × 100%
Multi-dimensional Assessment
We evaluate models across multiple dimensions:
- Generation Quality: Assessing the quality and accuracy of initially generated images
- Editing Consistency: Evaluating whether edits preserve unmodified elements while changing specified aspects
- Visual Understanding: Testing comprehension through multiple-choice questions about visual content
- Instruction Following: Measuring adherence to complex, multi-step instructions
UmniBench Leaderboard
🏆 Full Capability Models
| Model | Turn 1 Avg⇅ | Turn 2 Avg⇅ | Turn 3 Avg⇅ | Overall Avg↓ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bagel-think | 87.39 | 80.03 | 66.58 | 77.85 |
| Ovis-U1 | 91.01 | 77.32 | 64.69 | 77.45 |
| Bagel | 86.54 | 76.47 | 62.95 | 75.14 |
| UniPic2 | 85.34 | 79.37 | 60.32 | 74.86 |
| GPT4o | 84.77 | 75.54 | 61.33 | 73.71 |
| OmniGen2 | 84.84 | 59.66 | 47.34 | 63.56 |
| OneCAT | 83.29 | 54.71 | 45.53 | 60.76 |
| Lumina-DiMOO | 76.20 | 42.45 | 38.47 | 51.90 |
🔍 Understanding Only Models
| Model | Turn 1 Avg⇅ | Turn 2 Avg⇅ | Turn 3 Avg⇅ | Overall Avg↓ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kimi-VL-A3B-Instruct | 86.83 | 76.47 | 62.68 | 75.14 |
| Januspro | 84.21 | 66.64 | 55.14 | 68.39 |
| Qwen3-VL-8B-Instruct | 85.62 | 64.01 | 52.05 | 66.89 |
| Emu3 | 79.89 | 56.69 | 47.75 | 61.10 |
| Janus | 48.09 | 40.87 | 34.10 | 40.90 |
| BLIP-VQA | 40.51 | 34.74 | 33.22 | 36.07 |
🎨 Generation Only Models
| Model | Turn 1 Avg⇅ | Turn 2 Avg⇅ | Turn 3 Avg⇅ | Overall Avg↓ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unipic | 85.62 | 68.29 | 58.56 | 70.56 |
| OneCat | 84.84 | 68.23 | 58.44 | 70.24 |
| Emu3 | 81.37 | 67.50 | 59.38 | 69.20 |
| JanusPro | 84.21 | 66.64 | 55.14 | 68.39 |
| PixArt-Alpha | 77.97 | 68.23 | 58.44 | 68.05 |
| Janus | 81.16 | 66.64 | 55.14 | 67.41 |
✏️ Editing Only Models
| Model | Turn 2 Avg⇅ | Turn 3 Avg⇅ | Overall Avg↓ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nano-Banana-Gemini | 77.02 | 70.18 | 73.68 |
| Qwen-Image-Edit | 80.82 | 64.09 | 72.54 |
| FLUX.1-Fill | 68.56 | 58.83 | 63.74 |
| InstructPix2Pix | 65.39 | 51.11 | 58.32 |
| MagicBrush | 64.01 | 52.05 | 58.09 |
| Step1X-Edit | 26.30 | 30.80 | 28.53 |
Key Findings
Finding 1: Significant Performance Degradation in Complex Reasoning Tasks
All evaluated unified multimodal models exhibit a consistent monotonic decline across the three evaluation stages. Average accuracy drops from 83.99% in the generation stage to 72.76% in the interaction stage, and finally to 59.55% in the counterfactual reasoning stage—a cumulative reduction of 29.1%. This reveals systematic challenges in long-horizon reasoning and adaptive capabilities. Notably, some models like OmniGen2 experience catastrophic performance degradation exceeding 44% from generation to counterfactual stages, evidencing severe robustness deficits when confronted with high-complexity counterfactual reasoning scenarios.
Finding 2: Domain-Specific Performance Gaps Reveal Architectural Limitations
Evaluation results show significant performance disparities across knowledge domains. Spatial relations (57.04%) and Plant (59.88%) form a high-complexity cluster, indicating fundamental architectural bottlenecks in current multimodal frameworks concerning three-dimensional spatial reasoning and fine-grained botanical feature extraction. Conversely, everyday domains like Household (79.89%), Gardening (76.69%), and Personal Care (75.93%) exhibit performance saturation. Interestingly, smaller models occasionally outperform larger counterparts in specific domains (e.g., GPT-4o surpasses Bagel-Think in Fluid dynamics), challenging the assumption that parameter scale universally dictates domain mastery.
Finding 3: Error Accumulation and Reasoning-Based Generation as Dual Bottlenecks
The low scores in counterfactual stages stem from two mechanisms: (1) Error Accumulation—since counterfactual stages use previously generated images as input, early-stage failures cascade forward, with noise in generated images amplifying through multiple editing rounds, manifesting as distorted textures and irregular colors; (2) Training Set Gap for Reasoning-Based Generation—training data primarily contains clear attribute descriptions, while interaction and counterfactual stages involve reasoning processes (e.g., predicting interaction outcomes after entity replacement) that are rare in training sets. This explains why tightly-coupled architectures with bidirectional token flow (e.g., Bagel-Think) demonstrate stronger reasoning stability.
Citation
@article{umnibench2025,
title={UmniBench: Unified Understand and Generation Model Oriented Omni-dimensional Benchmark},
author={Liu, Kai and Chen, Leyang and Li, Wenbo and Chen, Zhikai and Wang, Zhixin and Pei, Renjing and Kong, Linghe and Zhang, Yulun},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:XXXX.XXXXX},
year={2025}
}UmniBench represents a critical step toward comprehensive evaluation of unified multi-modal models. By testing generation, editing, and understanding in an integrated workflow, we provide insights into models' true capabilities for iterative visual-textual interactions.